In vitro Cytotoxicity Assay with Direct Cell Contact

In vitro Cytotoxicity Assay with Direct Cell Contact
(mouse cell line L929)
The Direct Cell Contact Test allows qualitative assessment of the cytotoxic potential of a test item according to ISO 10993-5. The test is performed by placing the test item on a monolayer of L929 cells. Cytotoxic substances released from the test item might cause deformation or even lysis of the cells beneath or around the test item, which can be evaluated microscopically.

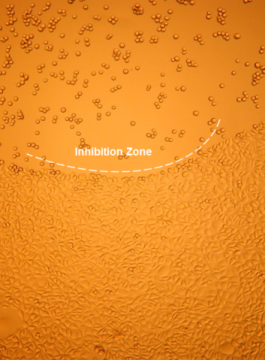
Assessment of Cytotoxicity by Microscopic Evaluation after Direct Cell Contact
- Test and control samples are placed on the pre-seeded cell monolayer without disturbing the integrity of the cell monolayer and incubated at 37 ± 1°C for at least 24 h.
- The malformation, degeneration, detachment or lysis of cells are used as measures for cytotoxicity. The biological reactivity is described and rated on a scale of 0 to 4 (see Table).
- The test item meets the requirements of the test, if the response to the test item is not greater than grade 2 (mildly reactive).


Protocol |
|
|
Cell line |
L929 cells (ATCC No. CCL1, NCTC clone 929 (connective tissue mouse), clone of strain L (DSMZ)) |
|
Analysis |
Microscopic evaluation |
|
Incubation time |
24 h at 37 ± 1°C |
|
Quality controls |
Solvent Control: DMEM 10% FBS Negative control: High-density polyethylene material (HDPE) Positive control: 0.1% Zinc-diethyldithiocarbamate (ZDEC) |
|
Data delivery |
Cytotoxicity according to grading scores |
|
Positive prediction |
The test item meets the requirements of the test, if the response to the test item is not greater than grade 2 (mildly reactive) |
References
- ISO 10993-5: 2009 “Tests for in vitro cytotoxicity”
- Autian, J. (1977). Toxicological evaluation of biomaterials: Primary acute toxicity screening program. Artif. Organs Vol 1, pp 53 – 60




